클러스터링
시계열 머신러닝 라이브러리 tslearn 설치
!pip install tslearn
Dynamic Time Warping
두 개의 시계열을 최대한 비슷하게 맞추는 경로를 찾음
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([1, 1.2, 1.3, 3, 1.6, 1.3])
y = np.array([1.2, 2.8, 2, 1.9, 1.7, 1.5])
plt.plot(x)
plt.plot(y)
output
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1ac03f9e0b0>]
<Figure size 640x480 with 1 Axes>
유사도만 계산
from tslearn.metrics import dtw, dtw_path
dtw_score = dtw(x, y)
dtw_score
output
0.6244997998398397
경로와 유사도를 모두 계산
optimal_path, dtw_score = dtw_path(x, y)
optimal_path
output
[(0, 0), (1, 0), (2, 0), (3, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5)]
발견한 경로에서 x와 y가 일치하는 것을 볼 수 있음
optimal_path = np.array(optimal_path)
plt.plot(x)
plt.plot(y)
for i in range(len(optimal_path)):
plt.plot(
optimal_path[i],
[x[optimal_path[i, 0]], y[optimal_path[i, 1]]],
color='gray', linestyle='dotted')
output
<Figure size 640x480 with 1 Axes>
Barycenter
무게중심(barycenter): 여러 개의 시계열 집합 가 있을 때, 이 집합에 속하는 모든 시계열과 DTW가 가장 짧은 시계열
DTW Barycenter Averaging (DBA) 알고리즘으로 찾을 수 있음
from tslearn.barycenters import dtw_barycenter_averaging
dataset = np.array([x, y])
b = dtw_barycenter_averaging(dataset)
plt.plot(x, linestyle='dotted')
plt.plot(y, linestyle='dotted')
plt.plot(b)
output
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x23ca0897eb0>]
<Figure size 640x480 with 1 Axes>
Soft-DTW
하나의 경로만 찾는 것이 아니라 여러 개의 경로를 부드럽게(soft) 합치는 방법
가 클 수록 더 부드러운 형태가 됨. 이면 DTW와 같음
from tslearn.metrics import soft_dtw_alignment
alignment, score = soft_dtw_alignment(x, y, gamma=0.5)
score
output
-0.5317286576835987
대체로 x의 0,1,2는 y의 0에 대응하고, x의 3은 y의 1에, x의 4는 y의 2, 3에 대응 (밝을 수록 더 강하게 대응)
plt.imshow(alignment, cmap='gray')
output
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x23ca0f47fa0>
<Figure size 640x480 with 1 Axes>
from tslearn.barycenters import softdtw_barycenter
b = softdtw_barycenter(dataset, gamma=0.5)
plt.plot(x, linestyle='dotted')
plt.plot(y, linestyle='dotted')
plt.plot(b)
output
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x23ca0feffa0>]
<Figure size 640x480 with 1 Axes>
클러스터링
여러 개의 데이터를 비슷한 것들끼리 하나의 클러스터(cluster, 군집)으로 묶는 비지도학습 방법
대표적으로 K-Means 클러스터링 알고리즘이 있음
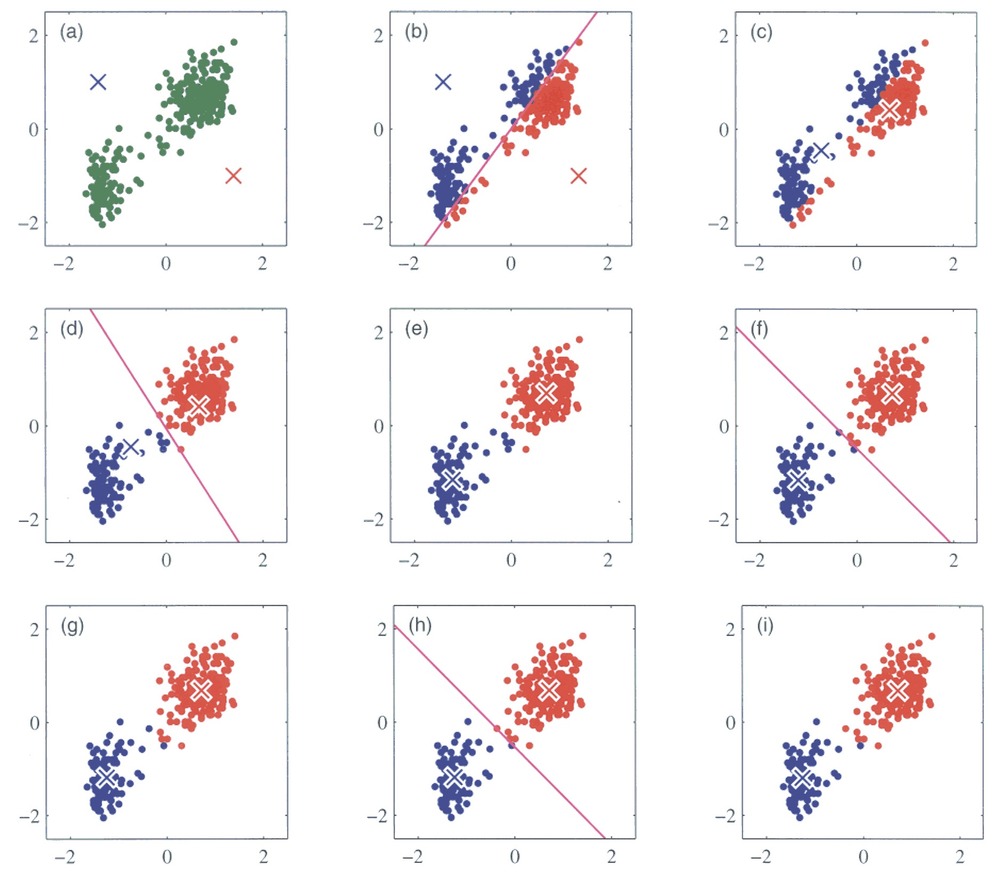
예제 데이터 준비
from tslearn.clustering import TimeSeriesKMeans
from tslearn.datasets import CachedDatasets
from tslearn.preprocessing import TimeSeriesScalerMeanVariance, \
TimeSeriesResampler
seed = 0
np.random.seed(seed)
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = CachedDatasets().load_dataset("Trace")
X_train = X_train[y_train < 4] # Keep first 3 classes
np.random.shuffle(X_train)
X_train = TimeSeriesScalerMeanVariance().fit_transform(X_train[:50])
X_train = TimeSeriesResampler(sz=40).fit_transform(X_train)
sz = X_train.shape[1]
유클리드 거리로 유사성 계산
km = TimeSeriesKMeans(n_clusters=3, verbose=True, random_state=seed)
y_pred = km.fit_predict(X_train)
plt.figure()
for yi in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, yi + 1)
for xx in X_train[y_pred == yi]:
plt.plot(xx.ravel(), "k-", alpha=.2)
plt.plot(km.cluster_centers_[yi].ravel(), "r-")
output
<Figure size 640x480 with 3 Axes>
DTW로 유사성 계산
dba_km = TimeSeriesKMeans(n_clusters=3,
n_init=2,
metric="dtw",
verbose=True,
max_iter_barycenter=10,
random_state=seed)
y_pred = dba_km.fit_predict(X_train)
for yi in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, yi + 1)
for xx in X_train[y_pred == yi]:
plt.plot(xx.ravel(), "k-", alpha=.2)
plt.plot(dba_km.cluster_centers_[yi].ravel(), "r-")
output
<Figure size 640x480 with 3 Axes>
Soft-DTW로 유사성 계산
sdtw_km = TimeSeriesKMeans(n_clusters=3,
metric="softdtw",
metric_params={"gamma": .01},
verbose=True,
random_state=seed)
y_pred = sdtw_km.fit_predict(X_train)
for yi in range(3):
plt.subplot(1, 3, yi + 1)
for xx in X_train[y_pred == yi]:
plt.plot(xx.ravel(), "k-", alpha=.2)
plt.plot(sdtw_km.cluster_centers_[yi].ravel(), "r-")
output
<Figure size 640x480 with 3 Axes>